The requirements of workpieces are ever increasing, consequently, the DEBURRING process is becoming more and more important. In addition to the cleaning systems, C-SYS I Cleaning Systems is also offering the deburring process at the same time.
Wherever there is mechanical machining, there will be a formation of a burr. During further machining or assembly, this burr can result in risk of injury, damage or malfunction of the component.
C-SYS I Cleaning Systems not only produces the deburring machine for mechanical brush deburring, but is also responsible for the respective DEBURRING process, which is being determined beforehand in a practical test. With this procedure there will be no nasty surprises when the machine has been completed.
Tools for mechanical deburring:
- Steel brushes (have an impact effect)
- Plastic brushes (have an abrasive effect)
- Burrs (removal of larger primary burrs)
- Mounted points
- Fabric washers
- Flush washers
- Polishing disks
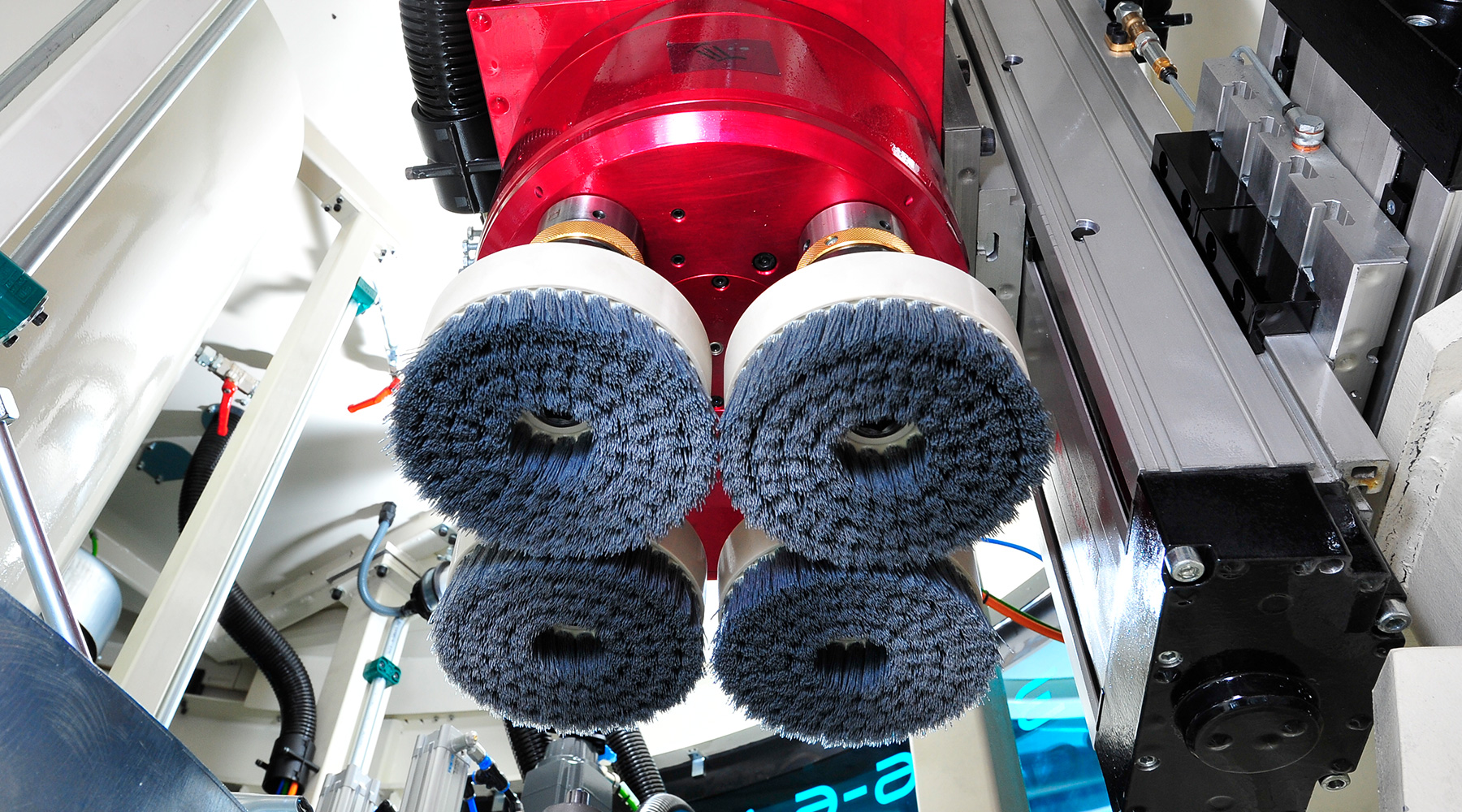
Deburring brush
With different dimensions of steel or plastic for brush deburring of edges that are difficult to access. The wear is automatically compensated via the control. The brushes are clamped in the machine by means of quick-change systems.
Internal deburring brush
Internal deburring by means of brushes, to compensate the wear of the brushes, new brushes are supplied via a magazine. For larger inside diameters, the wear can also be compensated by means of automatic correction via the control.
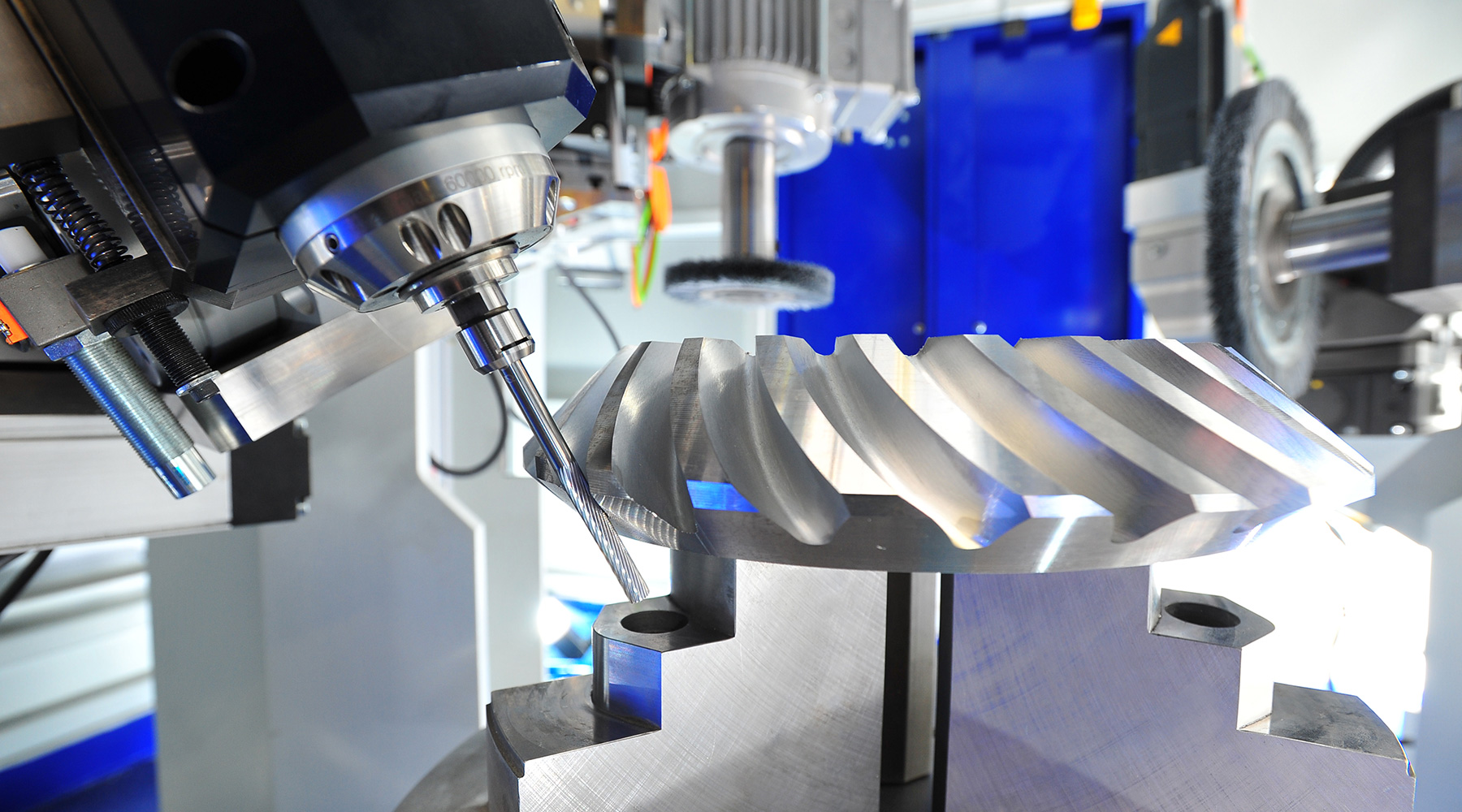
Burr
For pre-deburring of interlocks and removal of large primary burrs. The burr is picked up by an electric high-frequency milling spindle, enabling it to operate with different speed. The burr follows the interlocking or can be positioned on an edge to be deburred in a targeted way.
Procedure
It is necessary to perform a test beforehand with regard to workpiece cleaning, which also applies to deburring. As it is very difficult to evaluate a burr, at least one practical test is performed by C-SYS I Cleaning System for almost 100% of each project, which proceeds as follows:
- Customer sends workpiece with burr
- C-SYS I Cleaning Systems application engineer prepares the test, selecting the appropriate tools
- The test is performed independently or with the customer present
- Logging of the test with respective measurement report
- Return of the (deburred / machined) workpieces for evaluation by the customer
The performed tests enable SEMA Technology Group to confirm the requested qualities and cycle times.
Wear compensation
As the air volume is minimal, air evacuation within the shortest time is possible. This means we can always achieve an excess of power of the vacuum pumps. This excess enables a repeated “intermediate ventilation” of the vacuum chamber or drying with permanent artificial leakage.
- Empirically calculated values, i.e. the wear burr is entered in the control and an automatic correction occurs
- Pressure control, here, pressure value is set in the control with which the tool presses on the component
- Current consumptions, here, a specific range is determined in which the current is to remain during processing – if it falls out of this range, the NC axis automatically readjusts
Machine types
Dry or wet machining with emulsion or oil is possible for all deburring machines. Preprocessing is crucial here, if the workpiece is wet or damp, it is recommended to also perform the deburring process with the same medium. If the workpiece is dry, the deburring process can also be performed dry for workpieces free of burrs.
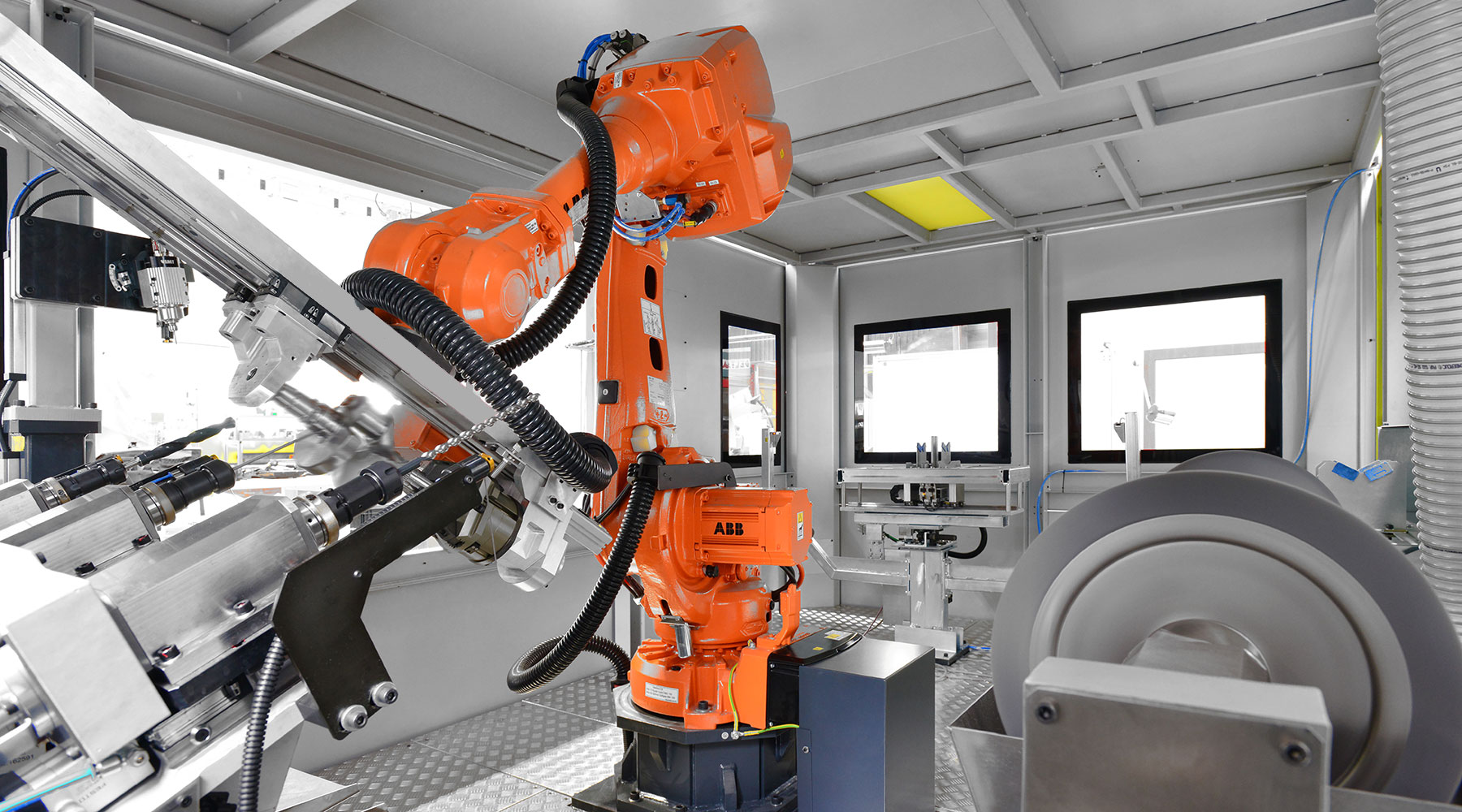
All machines can be automated via a gantry,robot, handling and delivery system- a basic discipline of the SEMA Technology Group.
Processing units used:
Arguments for mechanical deburring:
- Flexible in the machining of workpiece families
- Cost-effective process
- Process reliability
- Exact edge break (in hundredths range)
- Short machining times
- Standard tools
- Low setup costs
- No or short retooling times
- Fast tool changeover with quick-change systems
Automotive (truck / passenger car)
- Motor: Crankcase, cylinder head, crankshaft, camshaft, connecting rod, balance shaft, turbocharger, pump housing, valve housing etc.
- Gear unit: Clutch housing, gear case, countershaft, drive shaft, gear shaft, gear wheels, shifting fork, shift lever, CV transmission shafts etc.
- Steering: Steering rack, steering gearbox etc.
- Drive: Drive shaft, cardan shaft, quick-release axle, thrust tube etc.
- Chassis: Steering knuckles, half-axis, U-joint crosses, wheel carriers, servo pump, pin fork, track rod end etc.
- Body: Special section tubes, air conditioning compressor elements etc.
- E-mobility (electric motor): Rotor shaft, stator, motor housing etc.
 DEUTSCH
DEUTSCH ENGLISH
ENGLISH